In the third in a series of Blog Posts about email security and deliverability, I set out to explain what DMARC is and why you should use it.
DMARC or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance Policy is the most recent addition to a suite of email authentication methods available to companies.
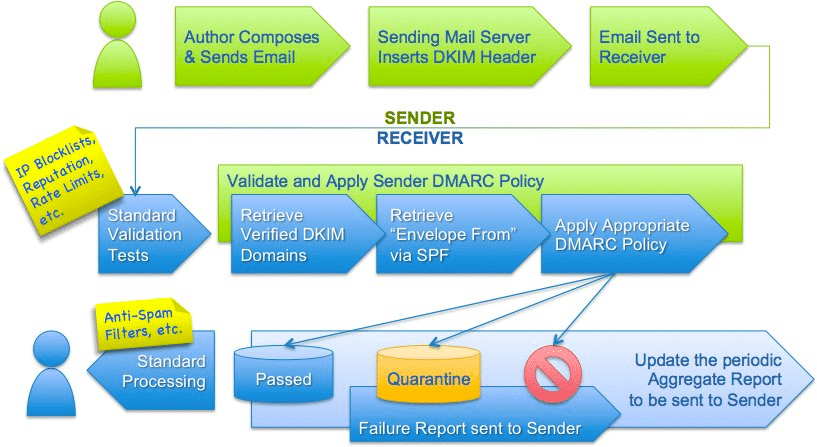
A DMARC policy allows a domain to inform a receiving mail server that their emails should be protected by SPF and DKIM. The DMARC Policy then informs the receiver what action should be taken if either of those authentication methods passes or fails. DMARC also provides a mechanism for a domain to request feedback about a sender’s domain and messages that have failed the DMARC evaluation, this allows for fault finding and further strengthens the system.
DMARC is designed to help email receivers determine if the incoming message aligns with the guidance issued by the sender. If not, DMARC includes guidance on how to handle messages that fail the sender’s domain policy. DMARC doesn’t directly advise a recipient whether or not an email is spam or otherwise fraudulent. Instead, DMARC requires that a message pass DKIM and SPF validation. This additional record ensures that a recipient knows which verification records to check for, the message must pass the SPF check and the domain in the From: header must match the domain used to validate SPF (must exactly match if strict alignment is specified). For DKIM, the message must be validly signed and the domain of the valid signature must align with the domain in the From: field (again must exactly match for strict alignment). Under DMARC a message can fail even if it passes SPF or DKIM but fails the alignment test, ie if it was sent from test.welgo.co.uk but the alignment specified is strict.
DMARC policies are published in the publicly accessible Domain Name System (DNS) records for your domain in the form of a specially formatted TXT record. If you have more than one mail server or system you would publish one record for each email system.
The receiver sends daily aggregated reports to an email address specified by the sender domain indicating to the sender domain administrator how many emails have been received and if these emails passed SPF and/or DKIM and were aligned or not. This allows the Sender domain administrator to assess the impact and effectiveness of the DKIM record during the deployment phase.
During the deployment phase there are a number of options which limit any negative effect such as, false positives specifying that messages should be quarantined opposed to rejected and setting the percentage of messages subjected to filtering.
By using DMARC with SPF and DKIM you allow the receiving mail system to verify that the mail is genuine thus increasing the odds that the email will pass that recipient’s spam filtering system. This is what we call “Increased Deliverability”. You also help to protect the reputation of your domain and decrease the chances of your domain being used in SPAM and Phishing attacks.
How does DMARC Work in practice?
If you are a Welgo Customer or a Welgo Google for Work Customer we will create a DMARC record for you. However we do not always do this as standard, this is because any third party systems you use to send email such as an email marketing system must be set up with your SPF and DKIM records before we can enable DMARC. Failing to do so would prevent emails from those systems reaching there intended recipients. If you have any questions about these records, would like DMARC Enabled or email security in general, please just call Welgo helpline on 0131 667 0195 or raise a support request via the Welgo Support Portal
If you are not already a Welgo Customer please call us and one of the team will be happy arrange an appointment to discuss how Welgo can help you with your Business IT needs.